// TRACE[ Overview | Extended Overview | People | Publications
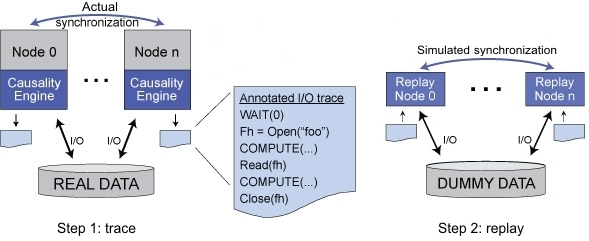
] THIS PAGE HAS MOVED. PLEASE UPDATE YOUR BOOKMARKS. IF YOU ARE NOT REDIRECTED IN A FEW SECONDS, PLEASE CLICK HERE TO GO TO OUR NEW PAGE. OverviewI/O traces play a critical role in storage systems evaluation. They are captured through a variety of mechanisms, analyzed to understand the characteristics and demands of different applications, and replayed against real and simulated storage systems to recreate representative workloads. Often, traces are much easier to work with than actual applications, particularly when the applications are complex to configure and run, or involve confidential data or algorithms. //TRACE is a new approach for extracting and replaying traces of parallel applications. Its tracing engine (the causality engine) automatically discovers inter-node data dependencies and inter-request compute times for each node (process) in an application. It does so by selectively delaying I/O in order to expose data dependencies among the compute nodes. The learned dependency information is saved in per-node annotated I/O traces. Such annotation allows a parallel replayer to closely mimic the behavior of a traced application.
PeopleFACULTY STAFF STUDENTS
Publications
|